Describe the Role of the Extracellular Matrix in Embryonic Development
Here we examine the role of the cell skeleton actin microtubules intermediate filaments in mediating matrix effects on. The main roles of the extracellular matrix ECM in the mature animal are to maintain the integrity and strength of organs and to provide the structural components of tissues such as bone cartilage and tendon.
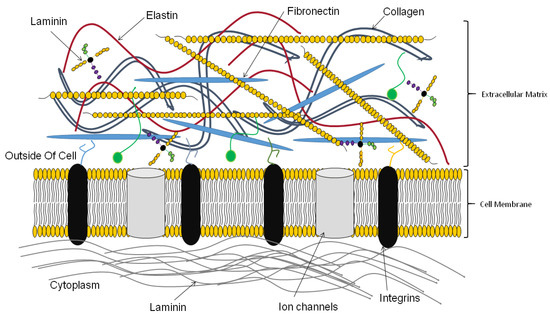
Ijms Free Full Text Recent Trends In Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Bioinks For 3d Printing An Updated Review Html
Describe the role of extracellular matrix and its dynamics in tissue regeneration.
. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages the composition of ECM varies between. Describe the sequential events of tissue and organ development during embryogenesis. In the present review we describe the major findings on the role of the extracellular matrix glycoprotein fibronectin and its corresponding integrin receptor in the locomotory behavior of neural crest cells.
The extracellular matrix ECM is synthesized and secreted by embryonic cells beginning at the earliest stages of development. The neural crest provides a useful paradigm for cell migration and modulations in cell adhesion during morphogenesis. Likewise how the ECM contributes to cellular mechanical responses has been.
Over the last three decades our understanding of the many diverse roles of the extracellular matrix ECM in mammalian biology has greatly advanced. Extracellular molecules are linked to one another by multiple binding domains and form a stable multifunctional matrix. In the present review we describe the major findings on the role of the extracellular matrix glycoprotein fibronectin and its corresponding integrin receptor in the locomotory behavior of neural crest cells.
As the crucial non-cellular component of tissues the extracellular matrix ECM provides both physical support and signaling regulation to cells. From Protocol to Patient aims to explain the scientific knowledge and emerging technology as well as the clinical application in different organ systems and diseases. However the role of the extracellular matrix ECM which provides mechanical support and is key to many cell signaling processes has not been fully studied during this process.
In vivo fibronectin is associated with the migratory. Cells respond to the extracellular matrix through plasma membrane receptors which include. The distribution of the extracellular matrix protein thrombospondin TSP in cleavage to egg cylinder staged mouse embryos and its role in trophoblast outgrowth from cultured blastocysts were examined.
In fertilized one- to four-cell embryos. Some ECM molecules provide a fibrillar environment around cells while others provide a sheet-like basement membrane scaffold beneath epithelial cells. At the same time the cardiomyocytes compact into a dense aligned and highly vascularized myocardium.
Researchers have been unable to capitalize on these instructive cues due to the limited. Scaffold design is that tissues undergo extensive extracellular matrix ECM remodeling during development which is thought to play a significant role in directing cellular behavior in the formation of functional tissue. In fact the extracellular matrix actually stores some cellular growth factors which are then released locally based on the physiological needs of the local tissue.
In vivo fibronectin is associated with the migratory. During embryonic development the heart undergoes complex morphogenesis from a liner tube into the four chambers consisting of ventricles atria and valves. TSP was present within the cytoplasm of unfertilized eggs.
The extracellular matrix directs the morphology of a tissue by interacting with cell-surface receptors and by binding to the surrounding growth factors that then incite signaling pathways. Their components have been well described in most species but our understanding of the mechanisms that control ECM remodeling remains limited. The extracellular matrix ECM plays an essential role in organizing tissues defining their shapes or in presenting growth factors.
The fibronectin-rich ECM appears to be critical to heart formation with distinct fibronectin fiber morphology associated with each stage of cardiac looping 9. Some ECM molecules provide a fibrillar environment around cells while others provide a sheet-like basement membrane scaffold beneath epithelial cells. The extracellular matrix interacts with cells and promotes and regulates cellular functions such as adhesion migration proliferation differentiation and morphogenesis.
The components of the extracellular matrix are usually the. The extracellular matrix is a network of fibrous proteins and proteoglycans that fills the space between the cells within your tissues. The ECM comes in a variety of forms including the more standard ECM that is internal to the animal and on the basal side of epithelial sheets as well as the apical ECM which is especially elaborated in the invertebrates to form the exoskeleton.
The extracellular matrix ECM is known to play an important role in this process but understanding. Our understanding of ECM composition structure and function has grown considerably in the last several decades and this knowledge has revealed that the extracellular microenvironment is critically important for cell growth survival. The ECM serves important structural and regulatory roles in establishing tissue architecture and cellular function.
The neural crest provides a useful paradigm for cell migration and modulations in cell adhesion during morphogenesis. In biology the extracellular matrix is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals such as collagen enzymes glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. This textbook Regenerative Medicine.
The extracellular matrix ECM and its receptors make diverse contributions to development. It is now well established that in addition to providing a scaffold for cells the ECM provides essential biochemical and biomechanical cues directing tissue morphogenesis during development. The field of regenerative medicine has developed rapidly over the past 20 years with the advent of molecular and cellular techniques.
In the developing embryo however ECM not only participates in the morphogenesis of these tissues but also has a series of other functions. As the crucial non-cellular component of tissues the extracellular matrix ECM provides both physical support and signaling regulation to cells. The extracellular matrix ECM is the non-cellular component of tissues throughout the body and is formed of filamentous proteins proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans.
During embryonic development the extracellular matrix ECM promotes the production of differentiated products by epithelial cells and the migration of mesenchymal cells and probably also plays a role in epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Role Played by Prx1-Dependent Extracellular Matrix Properties in Vascular Smooth Muscle Development in Embryonic Lungs April 2015 Pulmonary Circulation 52000-000. Enable to give examples on the role of growth factors and extracellular matrix molecules in organogenesis.
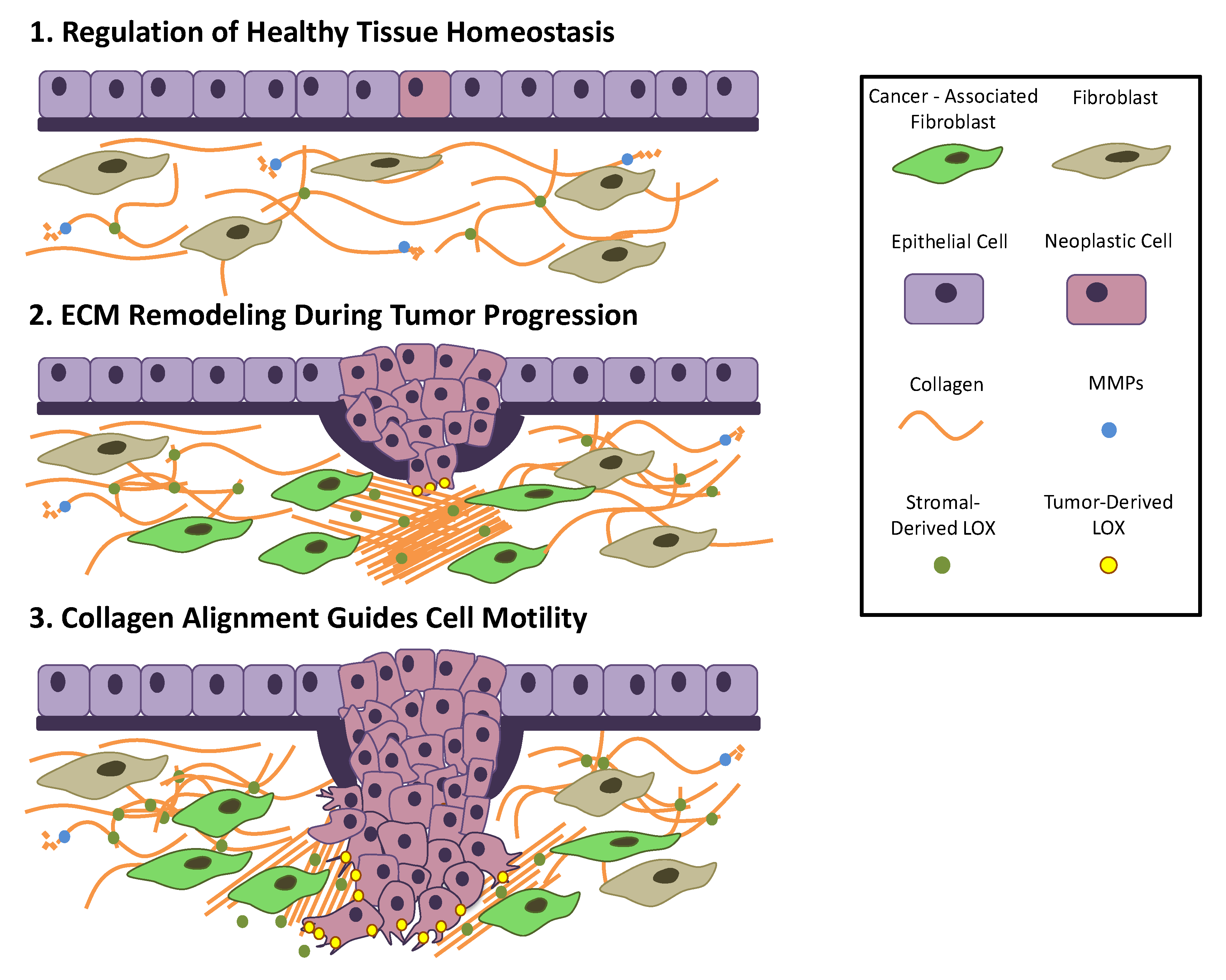
Cancers Free Full Text The Functional Role Of Extracellular Matrix Proteins In Cancer Html

Schematic For Production Of Extracellular Matrix Ecm Composites With Download Scientific Diagram
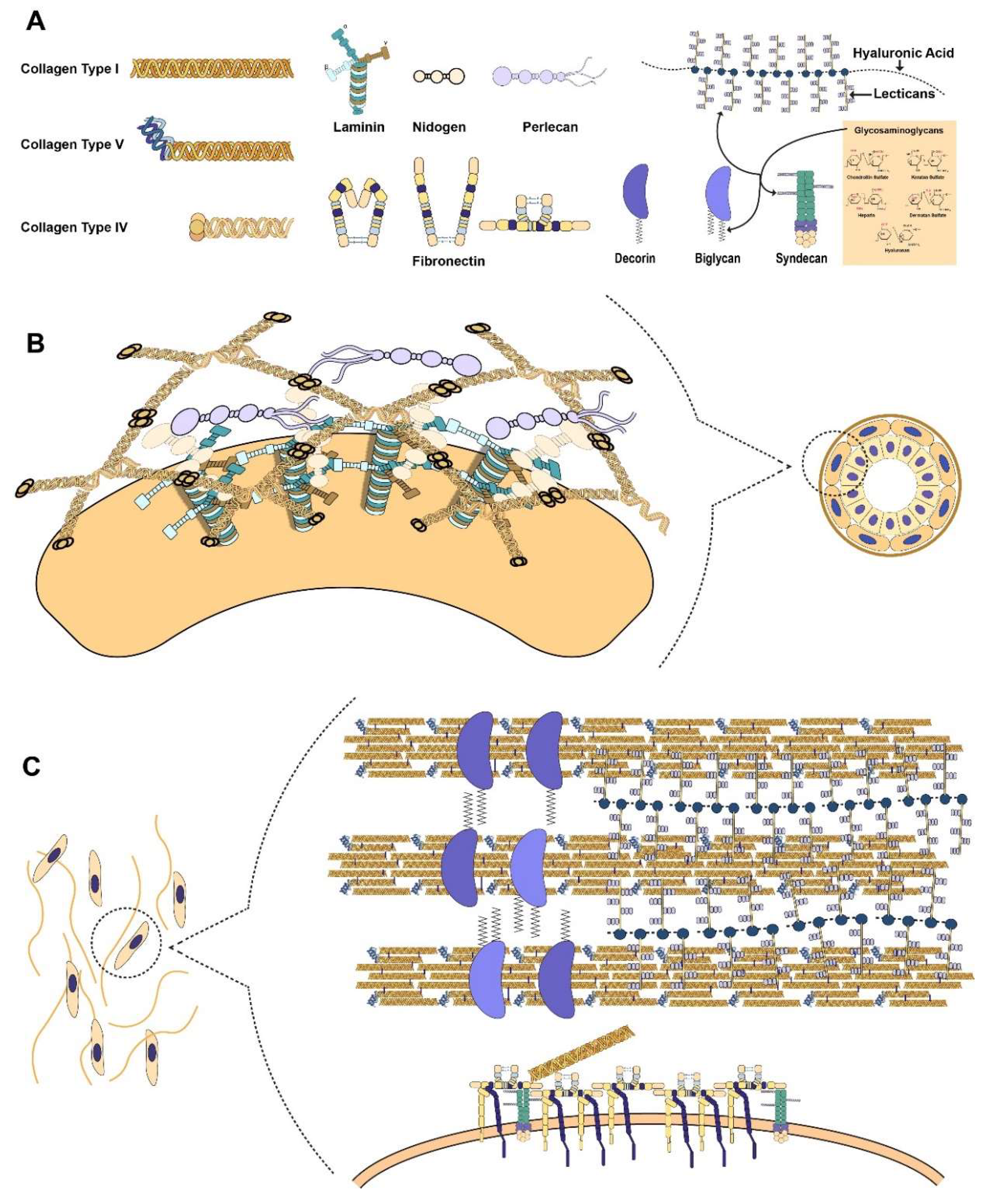
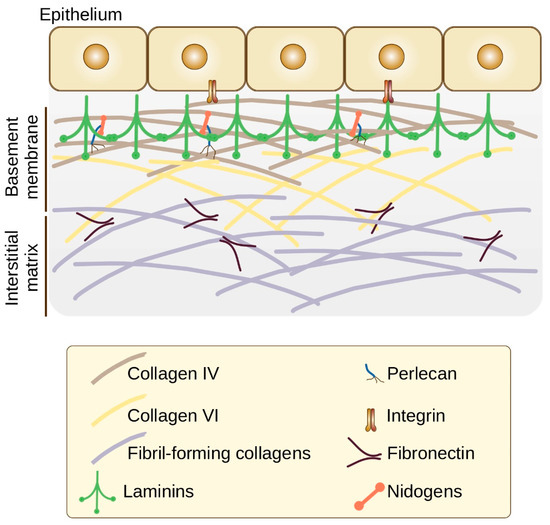
Ijms Free Full Text Role Of Extracellular Matrix In Development And Cancer Progression Html

There Are Several Physical Properties Of The Extracellular Matrix Ecm Download Scientific Diagram

Extracellular Matrix Definition Function Components Biology Dictionary What Is Collagen Collagen Ideal Shape

39 Extracellular Matrix Glycosaminoglycans And Proteoglycans Basicmedical Key

Example Of Extracellular Matrix Ecm Implications The Extracellular Download Scientific Diagram

Schematic For Production Of Extracellular Matrix Ecm Composites With Download Scientific Diagram
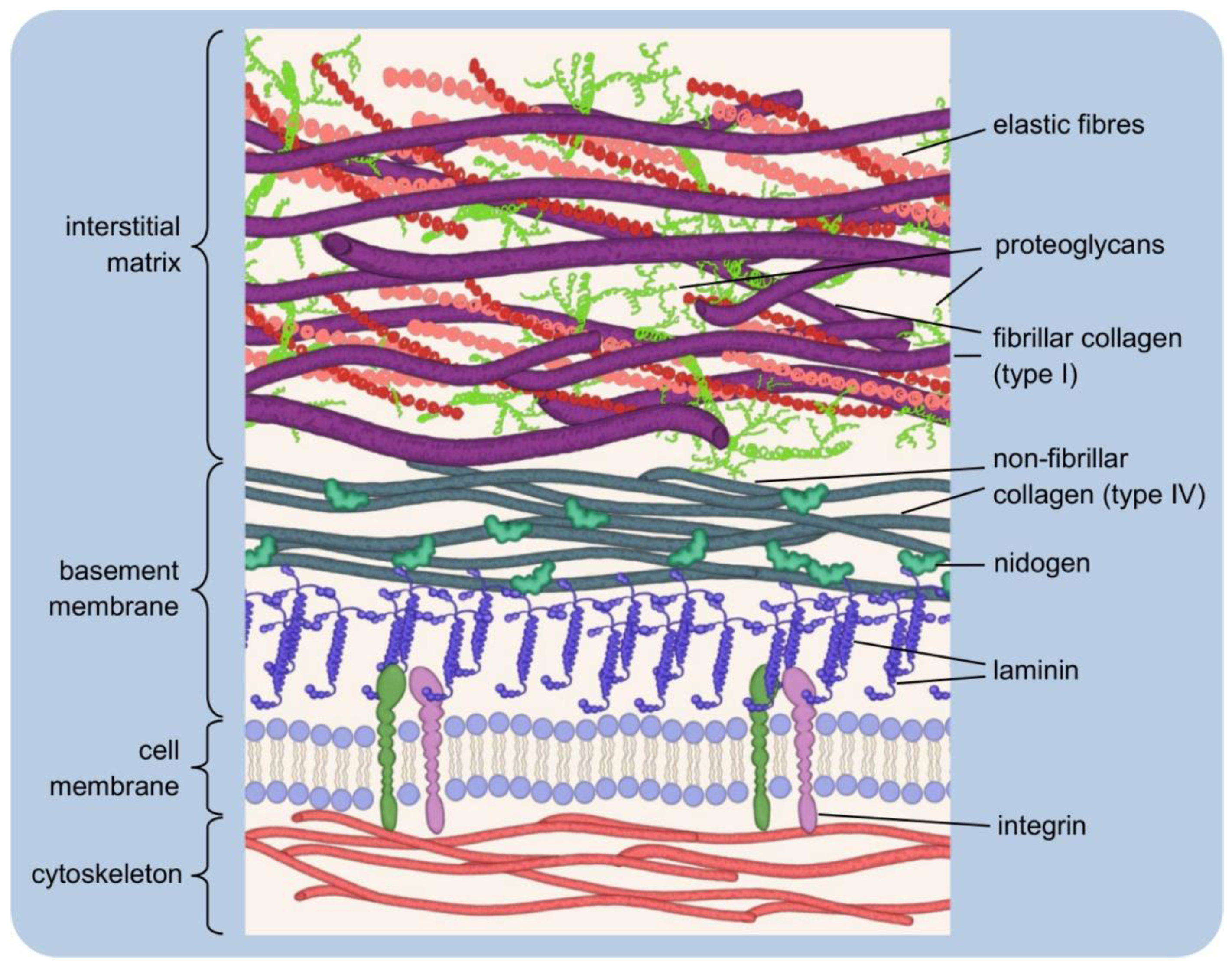
Cells Free Full Text Into The Tissues Extracellular Matrix And Its Artificial Substitutes Cell Signalling Mechanisms Html

Major Components Of The Extracellular Matrix Ecm Transmembrane Download Scientific Diagram
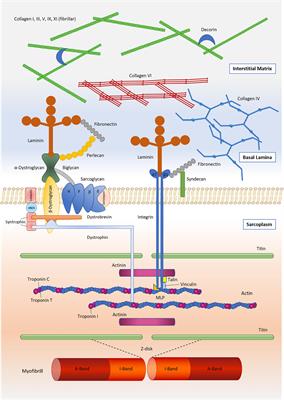
Frontiers Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix What Do We Know About Its Composition Regulation And Physiological Roles A Narrative Review Physiology

Ijms Free Full Text Role Of Extracellular Matrix In Development And Cancer Progression Html

Extracellular Matrix Mimics Using Hyaluronan Based Biomaterials Trends In Biotechnology

Extracellular Matrix Mimics Using Hyaluronan Based Biomaterials Trends In Biotechnology

What Is The Mechanism By Which An Extra Cellular Matrix Is Produced By Cells Quora
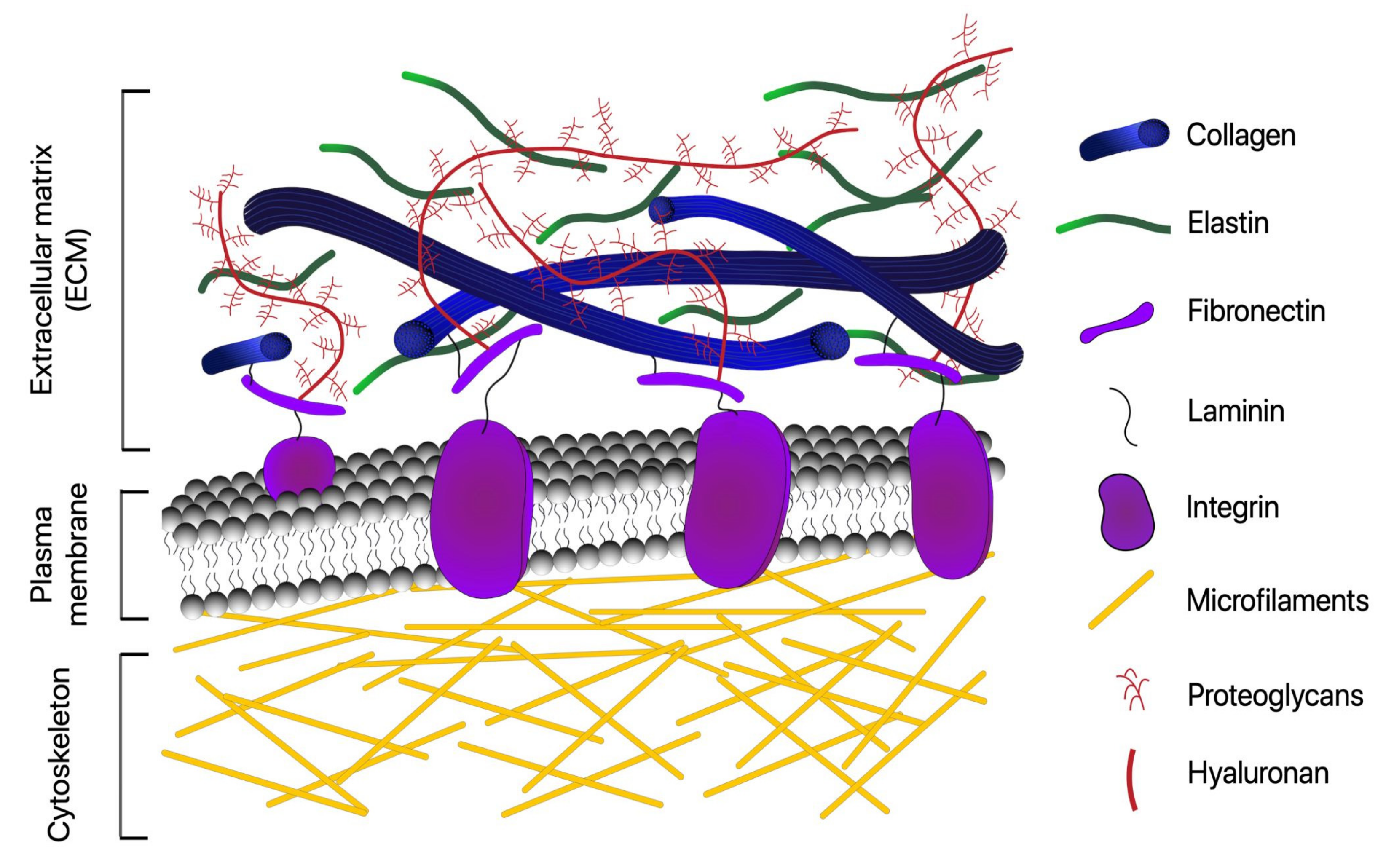
Cells Free Full Text Optical Microscopy And The Extracellular Matrix Structure A Review Html

Pdf The Impact Of The Extracellular Matrix On Inflammation Semantic Scholar


Comments
Post a Comment